We often see older people with thyroid problems so we don’t realize that it can also affect teenagers. But this is a real threat to your health and should be taken care of.
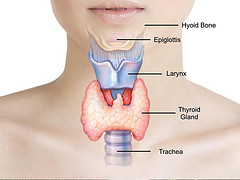
Your thyroid gland is a small gland located in the lower front of your neck. This gland is barely visible unless you are very thin, thyroid gland produces Thyroxin hormone, a chemical substance needed for proper functioning of many of your organs.
When the thyroid gland produces less or excess levels of thyroxin, you are prone to illness. An excessively enlarged thyroid gland can occur during thyroxin deficiency, excess or even with normal thyroxin levels, especially during your growth spurt. Therefore, it is essential to know more about thyroid disorders to stay in good health now and in the future.
Let’s begin by understanding the different types of thyroid disorders that can affect teens:
This is a condition caused by inadequate amounts of the thyroxin hormone in your body. You can either be born with this problem (Congenital Hypothyroidism) or you can acquire it later on as a child, teen or as an adult.
-
The later type occurs when your thyroid gland is damaged, usually triggered by a viral infection. This type of infection can happen at any age, but most commonly during adolescence or your teen years. Women are 4 to 7 times more likely to be affected than boys.Further, when the body's immune system attacks the cells in the thyroid gland, this is a condition that prevents the thyroid from producing hormones. The thyroid responds by working harder to make enough hormones. This can make it become enlarged and may result in a goiter.
If you have hypothyroidism, you may feel a combination of the following symptoms:
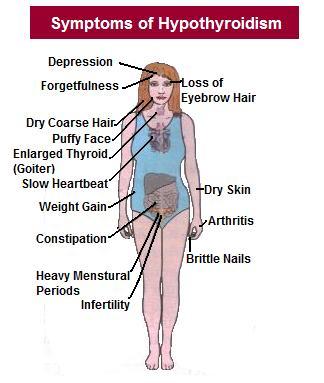 |
|
-
-If you have one or more of the above symptoms please talk to your parents and contact your doctor immediately.
-Your doctor will perform a blood test to confirm your thyroid status.
-As a course of treatment, you will be given Thyroxin tablets which might have to be continued throughout your life. The tablets need to be taken early in the morning, before meals/on an empty stomach and is recommended that they be stored away from direct sunlight.
-If you visit a doctor for any other reason while you are on thyroxin tablets, it is essential that you tell your doctor about this before he/she prescribes any other medication.SymptomsHaving hyperthyroidism means you may have one or more of the following symptoms and should contact a medical professional for advice on management:
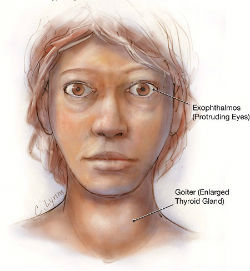 |
|
Treatment
-If you visit a doctor with the above symptoms, they will order a simple blood test to determine the thyroxin levels in your blood
-If hyperthyroidism is confirmed, you will be treated with anti-thyroid medication such as Carbimazole to reduce the excessive production of thyroid hormone in your body
-You may also be given a drug called Propranolol to reduce certain symptoms such as palpitations
-In certain extreme cases of hyperthyroidism, radio iodine treatment or surgery may be considered